Revisions for Infragram Media
| 51 CURRENT | liz |
October 16, 2020 17:12
| over 4 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Infragram.orgRead more at http://infragram.org Infragram WebcamInfragram DIY Filter PackInfrared images
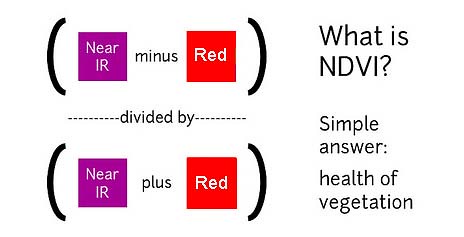
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
CameraThese are photos of prototypes; the camera has not yet been released as of Oct 2013. Prototypes
|
Revert | |
| 50 | warren |
July 01, 2014 20:42
| over 10 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Infragram.orgRead more at http://infragram.org Infragram WebcamInfragram DIY Filter PackInfrared images
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
CameraThese are photos of prototypes; the camera has not yet been released as of Oct 2013. Prototypes
|
Revert | |
| 49 | warren |
October 10, 2013 14:00
| over 11 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Infragram.orgRead more at http://infragram.org Infragram DIY Filter PackInfrared images
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
CameraThese are photos of prototypes; the camera has not yet been released as of Oct 2013. Prototypes
|
Revert | |
| 48 | warren |
October 10, 2013 14:00
| over 11 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Infragram.orgRead more at http://infragram.org Infragram DIY Filter PackInfrared images
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
CameraThese are photos of prototypes; the camera has not yet been released as of Oct 2013. Prototypes
|
Revert | |
| 47 | warren |
October 10, 2013 14:00
| over 11 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Infragram.orgRead more at http://infragram.org Infragram DIY Filter PackInfrared images
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
CameraThese are photos of prototypes; the camera has not yet been released as of Oct 2013. Prototypes
|
Revert | |
| 46 | warren |
October 10, 2013 13:59
| over 11 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Infragram.orgRead more at http://infragram.org Infragram DIY Filter PackInfrared images
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
CameraThese are photos of prototypes; the camera has not yet been released as of Oct 2013. Prototypes
|
Revert | |
| 45 | warren |
June 04, 2013 16:18
| over 11 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project CameraInfrared images
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Prototypes
|
Revert | |
| 44 | warren |
May 28, 2013 16:38
| over 11 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project CameraInfrared images
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Prototypes
|
Revert | |
| 43 | warren |
May 28, 2013 14:21
| over 11 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project CameraInfrared images
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Prototypes
|
Revert | |
| 42 | warren |
May 22, 2013 13:01
| almost 12 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
CameraInfrared images
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Prototypes
|
Revert | |
| 41 | warren |
May 22, 2013 12:58
| almost 12 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
CameraInfrared images
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
|
Revert | |
| 40 | warren |
May 22, 2013 12:58
| almost 12 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
CameraInfrared images
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
|
Revert | |
| 39 | donblair |
May 17, 2013 23:57
| almost 12 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
|
Revert | |
| 38 | cfastie |
May 15, 2013 19:27
| almost 12 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 8-10 images. NDVI images were derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, brown vegetation, and buildings have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
|
Revert | |
| 37 | cfastie |
May 15, 2013 19:22
| almost 12 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (RGB), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (VIS), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images. NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
|
Revert | |
| 36 | cfastie |
May 15, 2013 19:14
| almost 12 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (bottom). NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (right) of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (right). NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
|
Revert | |
| 35 | cfastie |
May 15, 2013 19:09
| almost 12 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (bottom).NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (right) of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (right). NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images (right). Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), false color infrared image (NRG), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images (right) of a yard, pond and adjacent saltmarsh in coastal Louisiana. Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 15-20 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that bare soil, dead vegetation, and boardwalks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
|
Revert | |
| 34 | cfastie |
May 15, 2013 19:07
| almost 12 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (bottom).NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (right) of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (right). NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), flase color infrared image (NRG), and grayscale and colorized normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) images (right). Aerial images were taken by a pair of synchronized cameras lofted by a kite and each is stitched from 12-15 images . NRG and NDVI images were derived from two photos, one taken by a normal camera and one taken by a camera modified to record only infrared light. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that brown vegetation has very low NDVI values because it is not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
|
Revert | |
| 33 | cfastie |
May 15, 2013 19:00
| almost 12 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (bottom).NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Note that tree trunks, brown grass, and rocks have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (right) of trailing arbutus. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that flowers have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (right). NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (right). NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. Note that tree trunks and brown vegetation have have very low NDVI values because they are not photosynthetic. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
|
Revert | |
| 32 | cfastie |
May 15, 2013 18:30
| almost 12 years ago
A collection of images for the Infragram plant health camera project
Caption: Normal color photo (top) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (bottom). Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single photo taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), superblue infrared photo (middle), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (right) of trailing arbutus. Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in the single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
Caption: Normal color photo (left), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) image (right). Healthy plants typically have NDVI values between 0.1 and 0.9. NDVI image was derived from two color channels in a single superblue photo which was taken with a camera modified with a special infrared filter. Images by Chris Fastie. Fullsize Image Link
|
Revert |








 (by Jeff Warren)
(by Jeff Warren)

























 (Mathew Lippincott)
(Mathew Lippincott)





