##Purpose##
Chemists use [expensive tools called spectrometers](/notes/warren/11-30-2011/visible-light-spectrometer-2660-4-7nm-bandwidth) (there are several kinds) to analyze unknown solid or liquid samples. We are working on a cheap version which we hope to use **to identify oil contamination in water and soil**, as well as a range of other possible toxins.
Spectrometers can also be used to identify species of plants or crop diseases, assess plumes from smokestacks, and have many other applications.
 ###What's spectrometry?###
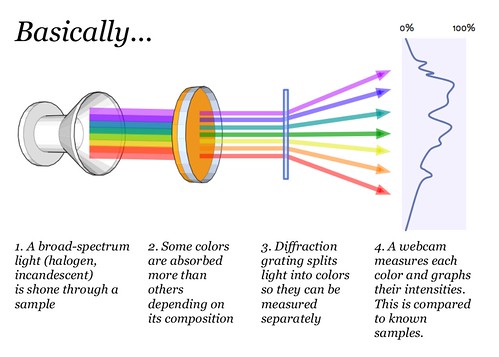
What we perceive as a single color consists of multiple blended colors- just as green paint can be made from mixing yellow and blue paint. A spectrometer is a device that splits light into the various colors it is composed of, which we otherwise cannot distinguish with the naked eye. By viewing a substance through a spectrometer, one can distinguish the exact mixture of colors, which correspond to specific wavelengths of light, that make up the perceived color of the sample.
###What's spectrometry?###
What we perceive as a single color consists of multiple blended colors- just as green paint can be made from mixing yellow and blue paint. A spectrometer is a device that splits light into the various colors it is composed of, which we otherwise cannot distinguish with the naked eye. By viewing a substance through a spectrometer, one can distinguish the exact mixture of colors, which correspond to specific wavelengths of light, that make up the perceived color of the sample.
 ##Make a spectrometer##
The PLOTS spectrometer is a Do-it-Yourself tool made from simple materials:
* 4 1/8" x 8 3/8" stiff black card paper
* a clean DVD-R
* a webcam
* velcro, dark tape, a box cutter/x-acto knife
The DVD's tightly packed grooves act as a diffraction grating -- basically a prism. When light enters, the different wavelengths of light are bent to different degrees, forming a rainbow -- a spectrum.
###[Video spectrometer construction »](/wiki/video-spectrometer-construction)###
The above link offers step-by-step instructions on making your own spectrometer. There is also a short [tutorial on how to take out the filter on the webcam](http://publiclaboratory.org/wiki/webcam-filter-removal) (optional). This design is released under the CERN Open Hardware License 1.1 (read agreement here). It features:
* around 400-900 nanometer range, maybe wider (what you can see with the naked eye, plus some infrared)
* 5-10 nm spectral resolution
* 20-30 samples per second
* ~ $10 in materials
* < 1 hour construction time
* [open-source software](/wiki/spectral-workbench)
Though these specs look pretty good, they still need to be compared rigorously with a traditional laboratory spectrometer. Are you interested in trying it?
##Using your spectrometer##
One group of toxins common to fossil fuel contamination are PAHs, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which are generally carcinogenic. We're trying to develop a step-by-step experimental procedure to prepare a soil or water sample, shine a full-spectrum light (like a halogen lamp) through it, and detect the missing wavelengths.
If you're interested, please chip in to develop and document a consistent way to read samples here:
###[Spectrometer usage »](/wiki/spectral-workbench-usage)###
We're also putting together a list of research (some of it our own) to draw upon in developing spectral analysis techniques for anything from soil to grapes to coffee:
###[Spectral Analysis »](/wiki/spectral-analysis)###
##Make a spectrometer##
The PLOTS spectrometer is a Do-it-Yourself tool made from simple materials:
* 4 1/8" x 8 3/8" stiff black card paper
* a clean DVD-R
* a webcam
* velcro, dark tape, a box cutter/x-acto knife
The DVD's tightly packed grooves act as a diffraction grating -- basically a prism. When light enters, the different wavelengths of light are bent to different degrees, forming a rainbow -- a spectrum.
###[Video spectrometer construction »](/wiki/video-spectrometer-construction)###
The above link offers step-by-step instructions on making your own spectrometer. There is also a short [tutorial on how to take out the filter on the webcam](http://publiclaboratory.org/wiki/webcam-filter-removal) (optional). This design is released under the CERN Open Hardware License 1.1 (read agreement here). It features:
* around 400-900 nanometer range, maybe wider (what you can see with the naked eye, plus some infrared)
* 5-10 nm spectral resolution
* 20-30 samples per second
* ~ $10 in materials
* < 1 hour construction time
* [open-source software](/wiki/spectral-workbench)
Though these specs look pretty good, they still need to be compared rigorously with a traditional laboratory spectrometer. Are you interested in trying it?
##Using your spectrometer##
One group of toxins common to fossil fuel contamination are PAHs, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which are generally carcinogenic. We're trying to develop a step-by-step experimental procedure to prepare a soil or water sample, shine a full-spectrum light (like a halogen lamp) through it, and detect the missing wavelengths.
If you're interested, please chip in to develop and document a consistent way to read samples here:
###[Spectrometer usage »](/wiki/spectral-workbench-usage)###
We're also putting together a list of research (some of it our own) to draw upon in developing spectral analysis techniques for anything from soil to grapes to coffee:
###[Spectral Analysis »](/wiki/spectral-analysis)###
 ###Online spectral analysis###
Along with the physical tool itself, the PLOTS team has also developed a [software suite](/wiki/spectral-workbench) and [online spectrum sharing website](https://spectralworkbench.org) which allows anyone to upload their data and work with others to try to interpret it. These tools are early prototypes and we're looking for help developing them.
Finally, a FAQ with some insights about actually *using* your spectrometer can be found here:
[Spectrometer FAQ](http://www.publiclaboratory.org/wiki/spectrometer-faq)
##Goals##
This is an early-stage, speculative project, but our goals include:
* Identify a contaminant in a sample, like a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon -- i.e. [naphthalene, anthracene or tetracene](http://publiclaboratory.org/notes/warren/8-5-2011/uv-visible-spectral-features-benzine-and-some-pahs). Tetracene has absorption bands well into the visible range.
* Identify a plant species by its spectrum. (see [this helpful paper by Zomer et al](https://publiclab.org/sites/default/files/Zomer_2009.PDF)) Or perhaps a mineral, using the [ASTER spectral library](http://archive.publiclaboratory.org/aster-spectral-library/)
* Try to identify something in a smokestack plume, like a refinery plume
###Older designs###
Several [older designs](/wiki/tube-spectrometer) have been documented on this site. Guides have been made showing you how to make some of these; they include:
* [plots-spectrometer-guide-small.pdf](http://www.publiclaboratory.org/sites/default/files/plots-spectrometer-guide-small.pdf) - by the PLOTS team for our workshop at the Whitney Museum
* [Make a Spectrometer.pdf](http://www.publiclaboratory.org/sites/default/files/Make%20a%20Spectrometer.pdf) - by Alex McCarthy
* [partsandcrafts-spectrometer-guide.pdf](http://archive.publiclaboratory.org/download/partsandcrafts-spectrometer-guide.pdf) - by [Parts and Crafts](http://partsandcrafts.org/) (21mb, print quality)
###Online spectral analysis###
Along with the physical tool itself, the PLOTS team has also developed a [software suite](/wiki/spectral-workbench) and [online spectrum sharing website](https://spectralworkbench.org) which allows anyone to upload their data and work with others to try to interpret it. These tools are early prototypes and we're looking for help developing them.
Finally, a FAQ with some insights about actually *using* your spectrometer can be found here:
[Spectrometer FAQ](http://www.publiclaboratory.org/wiki/spectrometer-faq)
##Goals##
This is an early-stage, speculative project, but our goals include:
* Identify a contaminant in a sample, like a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon -- i.e. [naphthalene, anthracene or tetracene](http://publiclaboratory.org/notes/warren/8-5-2011/uv-visible-spectral-features-benzine-and-some-pahs). Tetracene has absorption bands well into the visible range.
* Identify a plant species by its spectrum. (see [this helpful paper by Zomer et al](https://publiclab.org/sites/default/files/Zomer_2009.PDF)) Or perhaps a mineral, using the [ASTER spectral library](http://archive.publiclaboratory.org/aster-spectral-library/)
* Try to identify something in a smokestack plume, like a refinery plume
###Older designs###
Several [older designs](/wiki/tube-spectrometer) have been documented on this site. Guides have been made showing you how to make some of these; they include:
* [plots-spectrometer-guide-small.pdf](http://www.publiclaboratory.org/sites/default/files/plots-spectrometer-guide-small.pdf) - by the PLOTS team for our workshop at the Whitney Museum
* [Make a Spectrometer.pdf](http://www.publiclaboratory.org/sites/default/files/Make%20a%20Spectrometer.pdf) - by Alex McCarthy
* [partsandcrafts-spectrometer-guide.pdf](http://archive.publiclaboratory.org/download/partsandcrafts-spectrometer-guide.pdf) - by [Parts and Crafts](http://partsandcrafts.org/) (21mb, print quality)

 ###What's spectrometry?###
What we perceive as a single color consists of multiple blended colors- just as green paint can be made from mixing yellow and blue paint. A spectrometer is a device that splits light into the various colors it is composed of, which we otherwise cannot distinguish with the naked eye. By viewing a substance through a spectrometer, one can distinguish the exact mixture of colors, which correspond to specific wavelengths of light, that make up the perceived color of the sample.
###What's spectrometry?###
What we perceive as a single color consists of multiple blended colors- just as green paint can be made from mixing yellow and blue paint. A spectrometer is a device that splits light into the various colors it is composed of, which we otherwise cannot distinguish with the naked eye. By viewing a substance through a spectrometer, one can distinguish the exact mixture of colors, which correspond to specific wavelengths of light, that make up the perceived color of the sample.
 ##Make a spectrometer##
The PLOTS spectrometer is a Do-it-Yourself tool made from simple materials:
* 4 1/8" x 8 3/8" stiff black card paper
* a clean DVD-R
* a webcam
* velcro, dark tape, a box cutter/x-acto knife
The DVD's tightly packed grooves act as a diffraction grating -- basically a prism. When light enters, the different wavelengths of light are bent to different degrees, forming a rainbow -- a spectrum.
###[Video spectrometer construction »](/wiki/video-spectrometer-construction)###
The above link offers step-by-step instructions on making your own spectrometer. There is also a short [tutorial on how to take out the filter on the webcam](http://publiclaboratory.org/wiki/webcam-filter-removal) (optional). This design is released under the CERN Open Hardware License 1.1 (read agreement here). It features:
* around 400-900 nanometer range, maybe wider (what you can see with the naked eye, plus some infrared)
* 5-10 nm spectral resolution
* 20-30 samples per second
* ~ $10 in materials
* < 1 hour construction time
* [open-source software](/wiki/spectral-workbench)
Though these specs look pretty good, they still need to be compared rigorously with a traditional laboratory spectrometer. Are you interested in trying it?
##Using your spectrometer##
One group of toxins common to fossil fuel contamination are PAHs, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which are generally carcinogenic. We're trying to develop a step-by-step experimental procedure to prepare a soil or water sample, shine a full-spectrum light (like a halogen lamp) through it, and detect the missing wavelengths.
If you're interested, please chip in to develop and document a consistent way to read samples here:
###[Spectrometer usage »](/wiki/spectral-workbench-usage)###
We're also putting together a list of research (some of it our own) to draw upon in developing spectral analysis techniques for anything from soil to grapes to coffee:
###[Spectral Analysis »](/wiki/spectral-analysis)###
##Make a spectrometer##
The PLOTS spectrometer is a Do-it-Yourself tool made from simple materials:
* 4 1/8" x 8 3/8" stiff black card paper
* a clean DVD-R
* a webcam
* velcro, dark tape, a box cutter/x-acto knife
The DVD's tightly packed grooves act as a diffraction grating -- basically a prism. When light enters, the different wavelengths of light are bent to different degrees, forming a rainbow -- a spectrum.
###[Video spectrometer construction »](/wiki/video-spectrometer-construction)###
The above link offers step-by-step instructions on making your own spectrometer. There is also a short [tutorial on how to take out the filter on the webcam](http://publiclaboratory.org/wiki/webcam-filter-removal) (optional). This design is released under the CERN Open Hardware License 1.1 (read agreement here). It features:
* around 400-900 nanometer range, maybe wider (what you can see with the naked eye, plus some infrared)
* 5-10 nm spectral resolution
* 20-30 samples per second
* ~ $10 in materials
* < 1 hour construction time
* [open-source software](/wiki/spectral-workbench)
Though these specs look pretty good, they still need to be compared rigorously with a traditional laboratory spectrometer. Are you interested in trying it?
##Using your spectrometer##
One group of toxins common to fossil fuel contamination are PAHs, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which are generally carcinogenic. We're trying to develop a step-by-step experimental procedure to prepare a soil or water sample, shine a full-spectrum light (like a halogen lamp) through it, and detect the missing wavelengths.
If you're interested, please chip in to develop and document a consistent way to read samples here:
###[Spectrometer usage »](/wiki/spectral-workbench-usage)###
We're also putting together a list of research (some of it our own) to draw upon in developing spectral analysis techniques for anything from soil to grapes to coffee:
###[Spectral Analysis »](/wiki/spectral-analysis)###
 ###Online spectral analysis###
Along with the physical tool itself, the PLOTS team has also developed a [software suite](/wiki/spectral-workbench) and [online spectrum sharing website](https://spectralworkbench.org) which allows anyone to upload their data and work with others to try to interpret it. These tools are early prototypes and we're looking for help developing them.
Finally, a FAQ with some insights about actually *using* your spectrometer can be found here:
[Spectrometer FAQ](http://www.publiclaboratory.org/wiki/spectrometer-faq)
##Goals##
This is an early-stage, speculative project, but our goals include:
* Identify a contaminant in a sample, like a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon -- i.e. [naphthalene, anthracene or tetracene](http://publiclaboratory.org/notes/warren/8-5-2011/uv-visible-spectral-features-benzine-and-some-pahs). Tetracene has absorption bands well into the visible range.
* Identify a plant species by its spectrum. (see [this helpful paper by Zomer et al](https://publiclab.org/sites/default/files/Zomer_2009.PDF)) Or perhaps a mineral, using the [ASTER spectral library](http://archive.publiclaboratory.org/aster-spectral-library/)
* Try to identify something in a smokestack plume, like a refinery plume
###Older designs###
Several [older designs](/wiki/tube-spectrometer) have been documented on this site. Guides have been made showing you how to make some of these; they include:
* [plots-spectrometer-guide-small.pdf](http://www.publiclaboratory.org/sites/default/files/plots-spectrometer-guide-small.pdf) - by the PLOTS team for our workshop at the Whitney Museum
* [Make a Spectrometer.pdf](http://www.publiclaboratory.org/sites/default/files/Make%20a%20Spectrometer.pdf) - by Alex McCarthy
* [partsandcrafts-spectrometer-guide.pdf](http://archive.publiclaboratory.org/download/partsandcrafts-spectrometer-guide.pdf) - by [Parts and Crafts](http://partsandcrafts.org/) (21mb, print quality)
###Online spectral analysis###
Along with the physical tool itself, the PLOTS team has also developed a [software suite](/wiki/spectral-workbench) and [online spectrum sharing website](https://spectralworkbench.org) which allows anyone to upload their data and work with others to try to interpret it. These tools are early prototypes and we're looking for help developing them.
Finally, a FAQ with some insights about actually *using* your spectrometer can be found here:
[Spectrometer FAQ](http://www.publiclaboratory.org/wiki/spectrometer-faq)
##Goals##
This is an early-stage, speculative project, but our goals include:
* Identify a contaminant in a sample, like a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon -- i.e. [naphthalene, anthracene or tetracene](http://publiclaboratory.org/notes/warren/8-5-2011/uv-visible-spectral-features-benzine-and-some-pahs). Tetracene has absorption bands well into the visible range.
* Identify a plant species by its spectrum. (see [this helpful paper by Zomer et al](https://publiclab.org/sites/default/files/Zomer_2009.PDF)) Or perhaps a mineral, using the [ASTER spectral library](http://archive.publiclaboratory.org/aster-spectral-library/)
* Try to identify something in a smokestack plume, like a refinery plume
###Older designs###
Several [older designs](/wiki/tube-spectrometer) have been documented on this site. Guides have been made showing you how to make some of these; they include:
* [plots-spectrometer-guide-small.pdf](http://www.publiclaboratory.org/sites/default/files/plots-spectrometer-guide-small.pdf) - by the PLOTS team for our workshop at the Whitney Museum
* [Make a Spectrometer.pdf](http://www.publiclaboratory.org/sites/default/files/Make%20a%20Spectrometer.pdf) - by Alex McCarthy
* [partsandcrafts-spectrometer-guide.pdf](http://archive.publiclaboratory.org/download/partsandcrafts-spectrometer-guide.pdf) - by [Parts and Crafts](http://partsandcrafts.org/) (21mb, print quality)